|
mlpack
master
|
|
mlpack
master
|
An implementation of LARS, a stage-wise homotopy-based algorithm for l1-regularized linear regression (LASSO) and l1+l2 regularized linear regression (Elastic Net). More...
Public Member Functions | |
| LARS (const bool useCholesky=false, const double lambda1=0.0, const double lambda2=0.0, const double tolerance=1e-16) | |
| Set the parameters to LARS. More... | |
| LARS (const bool useCholesky, const arma::mat &gramMatrix, const double lambda1=0.0, const double lambda2=0.0, const double tolerance=1e-16) | |
| Set the parameters to LARS, and pass in a precalculated Gram matrix. More... | |
| const std::vector< size_t > & | ActiveSet () const |
| Access the set of active dimensions. More... | |
| const std::vector< arma::vec > & | BetaPath () const |
| Access the set of coefficients after each iteration; the solution is the last element. More... | |
| const std::vector< double > & | LambdaPath () const |
| Access the set of values for lambda1 after each iteration; the solution is the last element. More... | |
| const arma::mat & | MatUtriCholFactor () const |
| Access the upper triangular cholesky factor. More... | |
| void | Predict (const arma::mat &points, arma::vec &predictions, const bool rowMajor=false) const |
| Predict y_i for each data point in the given data matrix, using the currently-trained LARS model (so make sure you run Regress() first). More... | |
| template<typename Archive > | |
| void | Serialize (Archive &ar, const unsigned int) |
| Serialize the LARS model. More... | |
| void | Train (const arma::mat &data, const arma::vec &responses, arma::vec &beta, const bool transposeData=true) |
| Run LARS. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | Activate (const size_t varInd) |
| Add dimension varInd to active set. More... | |
| void | CholeskyDelete (const size_t colToKill) |
| void | CholeskyInsert (const arma::vec &newX, const arma::mat &X) |
| void | CholeskyInsert (double sqNormNewX, const arma::vec &newGramCol) |
| void | ComputeYHatDirection (const arma::mat &matX, const arma::vec &betaDirection, arma::vec &yHatDirection) |
| void | Deactivate (const size_t activeVarInd) |
| Remove activeVarInd'th element from active set. More... | |
| void | GivensRotate (const arma::vec::fixed< 2 > &x, arma::vec::fixed< 2 > &rotatedX, arma::mat &G) |
| void | Ignore (const size_t varInd) |
| Add dimension varInd to ignores set (never removed). More... | |
| void | InterpolateBeta () |
Private Attributes | |
| std::vector< size_t > | activeSet |
| Active set of dimensions. More... | |
| std::vector< arma::vec > | betaPath |
| Solution path. More... | |
| bool | elasticNet |
| True if this is the elastic net problem. More... | |
| std::vector< size_t > | ignoreSet |
| Set of ignored variables (for dimensions in span{active set dimensions}). More... | |
| std::vector< bool > | isActive |
| Active set membership indicator (for each dimension). More... | |
| std::vector< bool > | isIgnored |
| Membership indicator for set of ignored variables. More... | |
| double | lambda1 |
| Regularization parameter for l1 penalty. More... | |
| double | lambda2 |
| Regularization parameter for l2 penalty. More... | |
| std::vector< double > | lambdaPath |
| Value of lambda_1 for each solution in solution path. More... | |
| bool | lasso |
| True if this is the LASSO problem. More... | |
| const arma::mat * | matGram |
| Pointer to the Gram matrix we will use. More... | |
| arma::mat | matGramInternal |
| Gram matrix. More... | |
| arma::mat | matUtriCholFactor |
| Upper triangular cholesky factor; initially 0x0 matrix. More... | |
| double | tolerance |
| Tolerance for main loop. More... | |
| bool | useCholesky |
| Whether or not to use Cholesky decomposition when solving linear system. More... | |
An implementation of LARS, a stage-wise homotopy-based algorithm for l1-regularized linear regression (LASSO) and l1+l2 regularized linear regression (Elastic Net).
Let 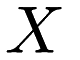 be a matrix where each row is a point and each column is a dimension and let
be a matrix where each row is a point and each column is a dimension and let 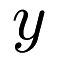 be a vector of responses.
be a vector of responses.
The Elastic Net problem is to solve
![\[ \min_{\beta} 0.5 || X \beta - y ||_2^2 + \lambda_1 || \beta ||_1 + 0.5 \lambda_2 || \beta ||_2^2 \]](form_80.png)
where  is the vector of regression coefficients.
is the vector of regression coefficients.
If 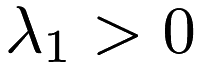 and
and 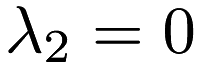 , the problem is the LASSO. If
, the problem is the LASSO. If 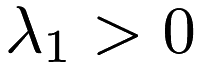 and
and 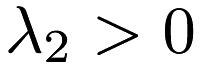 , the problem is the elastic net. If
, the problem is the elastic net. If 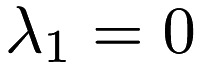 and
and 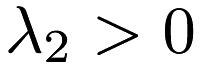 , the problem is ridge regression. If
, the problem is ridge regression. If 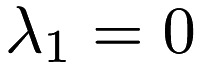 and
and 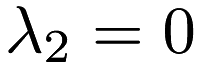 , the problem is unregularized linear regression.
, the problem is unregularized linear regression.
Note: This algorithm is not recommended for use (in terms of efficiency) when 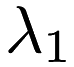 = 0.
= 0.
For more details, see the following papers:
| mlpack::regression::LARS::LARS | ( | const bool | useCholesky = false, |
| const double | lambda1 = 0.0, |
||
| const double | lambda2 = 0.0, |
||
| const double | tolerance = 1e-16 |
||
| ) |
Set the parameters to LARS.
Both lambda1 and lambda2 default to 0.
| useCholesky | Whether or not to use Cholesky decomposition when solving linear system (as opposed to using the full Gram matrix). |
| lambda1 | Regularization parameter for l1-norm penalty. |
| lambda2 | Regularization parameter for l2-norm penalty. |
| tolerance | Run until the maximum correlation of elements in (X^T y) is less than this. |
| mlpack::regression::LARS::LARS | ( | const bool | useCholesky, |
| const arma::mat & | gramMatrix, | ||
| const double | lambda1 = 0.0, |
||
| const double | lambda2 = 0.0, |
||
| const double | tolerance = 1e-16 |
||
| ) |
Set the parameters to LARS, and pass in a precalculated Gram matrix.
Both lambda1 and lambda2 default to 0.
| useCholesky | Whether or not to use Cholesky decomposition when solving linear system (as opposed to using the full Gram matrix). |
| gramMatrix | Gram matrix. |
| lambda1 | Regularization parameter for l1-norm penalty. |
| lambda2 | Regularization parameter for l2-norm penalty. |
| tolerance | Run until the maximum correlation of elements in (X^T y) is less than this. |
|
private |
Add dimension varInd to active set.
| varInd | Dimension to add to active set. |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
Remove activeVarInd'th element from active set.
| activeVarInd | Index of element to remove from active set. |
|
private |
|
private |
Add dimension varInd to ignores set (never removed).
| varInd | Dimension to add to ignores set. |
|
private |
|
inline |
Access the set of values for lambda1 after each iteration; the solution is the last element.
Definition at line 166 of file lars.hpp.
References lambdaPath.
|
inline |
Access the upper triangular cholesky factor.
Definition at line 169 of file lars.hpp.
References matUtriCholFactor, and Serialize().
| void mlpack::regression::LARS::Predict | ( | const arma::mat & | points, |
| arma::vec & | predictions, | ||
| const bool | rowMajor = false |
||
| ) | const |
Predict y_i for each data point in the given data matrix, using the currently-trained LARS model (so make sure you run Regress() first).
If the data matrix is row-major (as opposed to the usual column-major format for mlpack matrices), set rowMajor = true to avoid an extra transpose.
| points | The data points to regress on. |
| predictions | y, which will contained calculated values on completion. |
| void mlpack::regression::LARS::Serialize | ( | Archive & | ar, |
| const unsigned | int | ||
| ) |
Serialize the LARS model.
Referenced by MatUtriCholFactor().
| void mlpack::regression::LARS::Train | ( | const arma::mat & | data, |
| const arma::vec & | responses, | ||
| arma::vec & | beta, | ||
| const bool | transposeData = true |
||
| ) |
Run LARS.
The input matrix (like all mlpack matrices) should be column-major – each column is an observation and each row is a dimension. However, because LARS is more efficient on a row-major matrix, this method will (internally) transpose the matrix. If this transposition is not necessary (i.e., you want to pass in a row-major matrix), pass 'false' for the transposeData parameter.
| data | Column-major input data (or row-major input data if rowMajor = true). |
| responses | A vector of targets. |
| beta | Vector to store the solution (the coefficients) in. |
| transposeData | Set to false if the data is row-major. |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
Value of lambda_1 for each solution in solution path.
Definition at line 207 of file lars.hpp.
Referenced by LambdaPath().
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
|
private |
Upper triangular cholesky factor; initially 0x0 matrix.
Definition at line 185 of file lars.hpp.
Referenced by MatUtriCholFactor().
|
private |
|
private |
 1.8.11
1.8.11